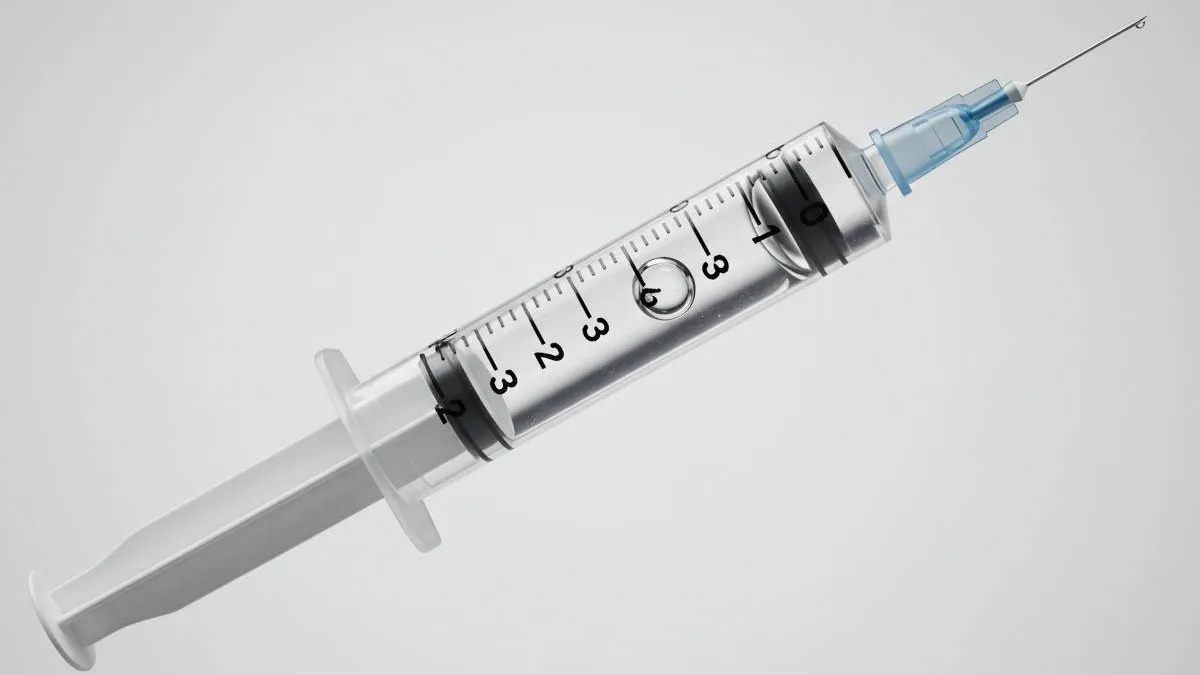
Giving an injection requires hygiene and precise technique; a syringe filled with air can cause pain, loss of medication effectiveness, and even air embolism.
Injecting with a syringe containing air can cause serious complications if the amount of air is high, although a small bubble does not represent a risk, according to specialists.
The main consequence of this medical error is air embolism, a condition in which air enters the bloodstream and can cause severe discomfort or, in extreme cases, death.
In addition to the life-threatening risk, injecting with air in the syringe can cause localized pain similar to a bump or bruise, as well as reduce the effectiveness of the medication if the dose is not applied correctly.
In this scenario, the drug could be administered incompletely or even lose some of its therapeutic properties.
However, experts emphasize that for serious complications to occur, a significant amount of air in the syringe is required.
A tiny bubble usually has no repercussions. In fact, in some medical cases, a small bubble is allowed to enter, as it can help provide additional support for the medication or serum being administered.
Recommendations for safe injections
The injection process must be performed with strict hygiene and technical care, both to protect the patient’s health and to ensure the drug’s effectiveness. These are the basic steps to follow:
- Choose the application area: thigh, hip, or upper arm.
- Check the medication: Check that the dose is correct and that the syringe is suitable.
- Wash your hands with soap and water before the procedure.
- Disinfect the skin with cotton and alcohol, and let it dry before inserting the needle.
- Give the injection by holding the muscle with your fingers and placing the needle straight into the muscle, then slowly push the medication in.
- Withdraw and press: Pull the syringe straight out and press the area with the same cotton used to clean the skin.
Proper injection administration not only prevents infection but also minimizes pain and ensures the patient receives the full dose of medication.





















+ There are no comments
Add yours