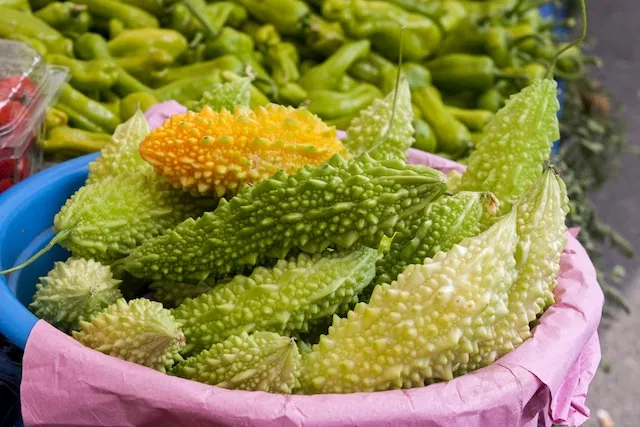
Cundeamor is a medicinal plant that can be used to complement the treatment of some skin problems, such as wounds and boils, as well as to help fight inflammation and prevent constipation.
Also known as bitter melon, St. Cajetan herb, or balsam pear, bitter melon has hypoglycemic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties.
Its scientific name is Momordica charantia, and it is generally found at fairs and municipal markets; it has a bitter taste and can be incorporated into juices, stews, and salads, as well as being used in the preparation of teas and compresses.
What is it for?
The indications and benefits of bitter melon are:
1. It helps control diabetes
Bittersweet has been used in traditional medicine to help control sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
This is because it contains bioactive compounds such as cucurbitan-type triterpenoids, including saponins and charantin, as well as peptides and polysaccharides, which could promote insulin release and sensitivity and protect pancreatic beta cells from oxidative stress.
2. Treats skin problems
Cundeamor is used topically to help treat skin problems such as wounds, burns, boils, and eczema, thanks to its healing, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties.
3. Prevents constipation
Consuming bitter melon in salads, stews, or soups, for example, helps prevent constipation because this non-conventional food plant (NCP) contains a good amount of fiber that increases the volume and hydration of the stool, facilitating evacuation.
4. It could help with weight loss
Bittersweet, in the form of teas or supplements, could contribute to weight loss thanks to its antihyperlipidemic and anti-obesity action, which helps to lower triglycerides and cholesterol, and reduce inflammation.
However, more studies in humans and over longer periods are needed to assess its potential benefits in this regard.
5. Helps reduce inflammation
Supplementation with bitter melon may help in the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as hyperuricemia, gout, and osteoarthritis, since this medicinal plant helps control the production of inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and IL-6.
Is bitter melon good for treating parasites?
Apparently, bitter melon has antiparasitic properties; however, more scientific studies are still needed to prove its effectiveness in humans, as studies have been conducted mainly on animals.
What diseases does it cure?
Like other medicinal plants, bitter melon cannot cure any disease, although it can help relieve symptoms and slow the progression of some conditions, without offering a definitive cure.
Main properties
The balsam pear has healing, anti-rheumatic, hypoglycemic, antibiotic, antiviral, antidiabetic, astringent, insecticidal, laxative, and purgative properties.
This is because it contains bioactive components such as alkaloids, charantin, flavonoids, glycosides, phenolics, tannins, and terpenoids.
This plant is rich in several saponins, including momordicin, momordicoside, karavilagenin, karaviloside, and kuguacin, all of which contribute to its healing properties. How to use
Bittersweet can be consumed in preparations such as juices, soups, pickles, salads, or stews, and can also be used in the form of teas or capsule supplements.
1. Balsam pear tea
Bittersweet tea is a traditional way to take advantage of the plant’s properties, both for general well-being and for skin care.
Ingredients
- 1 tablespoon of bitter melon leaves;
- 1 cup of boiling water.
Preparation method
To prepare bitter melon tea, boil the water in a kettle, turn off the heat, place the bitter melon leaves in a cup with the water, cover, and let it steep for 10 minutes.
Then it is strained, and you can drink 2 to 3 cups a day for up to 8 weeks, following the guidance of a doctor or herbalist.
This same tea can also be applied as a compress to the skin in case of injuries, wounds, scabies, or eczema.
2. Culinary Recipes
The bitter melon has a very bitter taste, and in the cuisine of some countries, it is consumed fresh in recipes such as juices, soups, salads, jams, pickles, or stews.
3. Balm capsules
Bittersweet is also available in capsules. However, this supplement should only be used under the guidance of a doctor or other healthcare professional experienced in medicinal plants.
Possible side effects
Cundeamor can cause side effects such as abdominal pain, stomach upset, intestinal gas, gastric ulcer, headache, vomiting, diarrhea, palpitations, nephritis, or vaginal bleeding.
When consumed in the form of tea or capsules, bitter melon can cause hypoglycemia, with symptoms such as tremors, weakness, cold sweats, paleness, blurred vision, palpitations, mental confusion, and drowsiness.
Contraindications
Bittersweet should not be used by people with allergies or hypersensitivity to plants of the Cucurbitaceae family or to the plant itself.
It is also not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, children, people with chronic diarrhea, hypoglycemia, liver problems, or glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) enzyme deficiency.
Those who use insulin or oral medications to control diabetes should consult a doctor before consuming bitter melon, as it may interact with these drugs and cause hypoglycemia.
In these cases, their intake should only be done under the guidance of a doctor or other health professional specializing in medicinal plants.