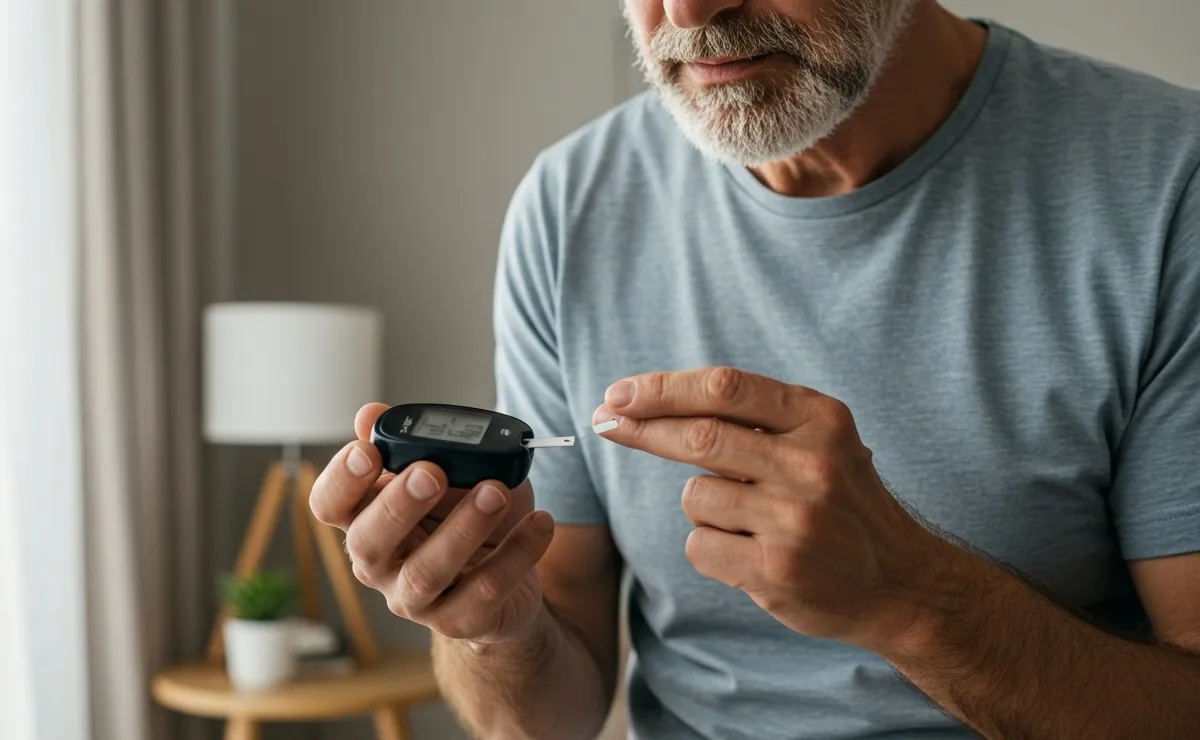
Waking up with blurred vision, intense thirst, or an urgent need to urinate may be more than just a passing inconvenience. These symptoms could indicate morning hyperglycemia, a common condition in people with diabetes that involves high blood sugar levels at the start of the day.
Hyperglycemia, if not controlled in time, can lead to serious complications such as kidney damage, neuropathies, or cardiovascular problems.
Therefore, recognizing its early signs is crucial to receiving timely medical attention and preventing irreversible consequences.
Main symptoms of hyperglycemia in the morning
- Blurred vision: One of the most common early signs. Excess glucose affects the blood vessels in the eyes, making it difficult to see when you wake up.
- Excessive thirst: The body reacts to high sugar levels by trying to eliminate them through urine, which causes dehydration and a persistent feeling of thirst.
- Frequent urination: Repeated visits to the bathroom, even at the beginning of the day, may be a response from the kidneys to filter excess glucose.
- Fatigue and weakness: Despite being well-rested, many people with morning hyperglycemia feel exhausted. This occurs because the body cannot properly use glucose as an energy source.
- Trouble concentrating: Excess sugar can also interfere with brain function, causing a lack of mental clarity and difficulty focusing.
Other warning signs of hyperglycemia
In addition to the above symptoms, there are additional manifestations that may occur:
- Headaches upon waking
- Tingling in the extremities
- Darkening of areas of the skin (particularly the neck or armpits)
- Frequent or recurrent infections
These signs should not be underestimated, as prolonged hyperglycemia can progress silently to the point of compromising vital organs.
Serious consequences of not treating hyperglycemia
Constantly maintaining high blood sugar levels can cause:
- Diabetic neuropathy: Nerve damage that causes numbness and pain, especially in the feet and hands.
- Nephropathy: Progressive deterioration of the kidneys that can lead to kidney failure.
- Diabetic retinopathy: Eye damage that could lead to blindness.
- Cardiovascular problems: High risk of heart attacks, hypertension, and strokes.
When to see a doctor?
According to Medline Plus, normal glucose levels should be between 90 and 130 mg/dL before eating and not exceed 180 mg/dL after meals. If fasting readings consistently range between 120 and 160 mg/dL, it’s essential to see a specialist.
A doctor can assess whether medication adjustments, insulin dosage modifications, or bedtime eating habits need to be reviewed to stabilize morning glucose levels.






















+ There are no comments
Add yours